Critical Chain Project Management(CCPM)
Critical Chain Project Management was developed and publicized by Dr. Eliyahu M. Goldratt in 1997. Followers of this methodology of Project Management claim it to be an alternative to the established standard of Project Management as advocated by PMBOK® and other standards of Project Management. In this article, we’ll provide a brief overview of what is Critical Chain Project Management, the principles of Critical Chain Project Management, and its applicability to managing projects across all organizations and verticals.
Are you looking forward to making a mark in the Project Management field? If yes, enroll in the PMP® Certification Training Course now and get a step closer to your career goal!
The Critical Chain Method has its roots in another one of Dr. Goldratt’s inventions: the Theory of Constraints (TOC). This project management method comes into force after the initial project schedule is prepared, which includes establishing task dependencies. The evolved critical path is reworked based on the Critical Chain Method. To do so, the methodology assumes constraints related to each task.
A Few of These Constraints Include
- There is a certain amount of uncertainty in each task.
- Task durations are often overestimated by team members or task owners. This is typically done to add a safety margin to the task so as to be certain of its completion in the decided duration.
- In most cases, the tasks should not take the time estimated, which includes the safety margin, and should be completed earlier.
- If the safety margin assumed is not needed, it is actually wasted. If the task is finished sooner, it may not necessarily mean that the successor task can start earlier as the resources required for the successor task may not be available until their scheduled time. In other words, the saved time cannot be passed on to finish the project early. On the other hand, if there are delays over and above the estimated schedules, these delays will most definitely get passed on, and, in most cases, will exponentially increase the project schedule.
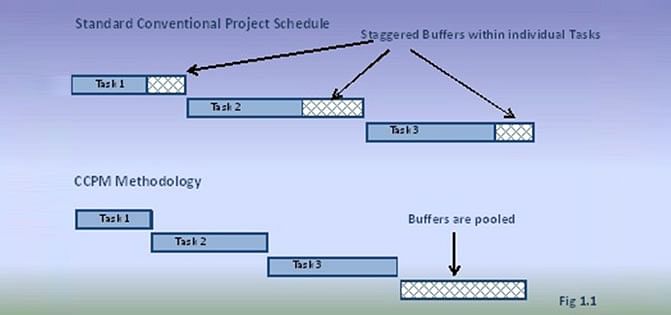
With the above assumptions, the Critical Path Methodology of project management recommends pooling of the task buffers and adding them at the end of the critical path:
| Want to become competent in core project management areas? Check out our PMP Certification Course Preview here. |
Critical Path Project Management Defines Three Types of Buffers
-
Project Buffer
The total pooled buffer depicted in the image above is referred to as the project buffer. -
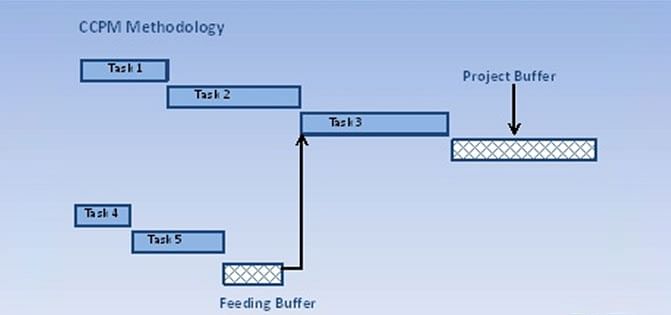
Feeding Buffer
In a project network, there are path/s which feed into the critical path. The pooled buffer on each such path represents the feeding buffer to the critical path (depicted in the image below), resulting in providing some slack to the critical path. -
Resource Buffer
This is a virtual task inserted just before critical chain tasks that require critical resources. This acts as a trigger point for the resource, indicating when the critical path is about to begin.
As the progress of the project is reported, the critical chain is recalculated. In fact, monitoring and controlling of the project primarily focused on the utilization of the buffers. As you can see, the critical chain method considers the basic critical path based project network and schedule to derive a completely new schedule.
The critical path project management methodology is very effective in organizations which do not have evolved project management practices.
However, the methodology does not advocate multi-tasking, and in projects with complex schedule networks, the results of implementing the critical path methodology have proven to be a deterrent to the overall project schedule. In addition, there is no standard method for calculating and optimizing the project buffers. The critical path project management methodology has had a fair amount of success in manufacturing; however, it has not achieved any noteworthy success in the IT industry.
Along similar lines, the event chain methodology of project management focuses on determining the uncertain events and the chain reactions they propagate. It is a method of modeling uncertainties and is based on Monte Carlo analysis, Bayesian Belief Network, and other established simulation methodologies. When they occur, events can cause other events, triggering an event chain, which will effectively alter the course of the project. Events and event chains are identified, and quantitative analysis is performed to determine the extent of the uncertainty and the probable impact of the same on the project. From this exercise, critical event chains are derived, which have the potential to impact the project significantly. Event chain diagrams are visual representations of events, event chains, and their impact.
It is clear that neither the critical path project management methodology nor the event chain methodology can be considered alternatives to the standard methodology for project management as advocated by PMBOK. While the critical path project management methodology can be at best used as a tool for deriving project schedule networks, the event chain methodology for project management can be used as a tool for quantitative risk analysis.
|
Find Our PMP Training in Top Cities |
Conclusion
If you are considering working toward your PMP® or PRINCE2® exam, Simplilearn offers a variety of project management courses that will help you pass, including the PRINCE2 Foundation Certification Training Course and the PMP Certification Training Course. Our PMP training courses are conducted by certified, highly experienced professionals with at least 10 years of experience.
Are you looking forward to making a mark in the Project Management field? If yes, enroll in the Project Management Certification Program now and get a step closer to your career goal!
PMP® and PMI® are registered trademarks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
Interested in learning more? View the video “Introduction to PMP Certification Training” below.
