Amidst the growing business market, there is an increased risk of mismanagement of data and endless possibilities of losing essential insights that hold the potential for driving growth.
Financial analytics works as a strong helper in eliminating financial mismanagement. It aids in drawing actionable insights to improve your business and increase profitability. The global financial analytics market has grown from $7.6 billion in 2020 and is expected to reach $19.8 billion by 2030. It is growing at a CAGR of 10.3%, which is a quick pace. Now is the right time to understand what financial analytics is and enter the industry.
What is Financial Analytics?
Financial analytics or finance analytics refers to the tools and processes used to observe datasets and get insights into an organization’s financial performance. It provides valuable details about an organization's financial data that helps make strategic decisions to improve its overall performance. When it comes to enterprise performance management and business intelligence, financial analytics significantly influences all aspects of the business. It plays an important role in the evaluation of profits, answering business-related queries, and future business forecasting.
Key Components of Financial Analytics
There are typically five key components of financial analytics, including:
1. Revenue
The quality, quantity, and revenue timings suggest long-term success. There are three elements related to revenues, i.e.,
Revenue growth: In revenue growth, the calculation does not involve one-time revenues that can result in distortion of analysis. Rather, it involves periodic calculation.

Revenue concentration: Suppose a customer is contributing a higher percentage of your revenue. In case that individual stops purchasing, you can get in financial trouble. Thus, ensuring no client can have more than 10% of your total revenue is wise.
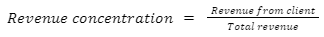
Revenue per employee: It represents a ratio that determines the business productivity. The higher the ratio, the better the productivity.

2. Profits
The consistency in monetary gain or profit, obtained after eliminating all the expenditures, is important to ensure the longevity of the business.
Gross profit margin: It allows us to control the cost of goods or revenue with no fear of losing the ability to pay off ongoing expenses.

Operating profit margin: It helps to discover an organization's capability to make a profit despite how finances are operated. Operations do not include taxes or interests.

Net profit margin: The remainder can be reinvested in the business or distributed to owners as dividends.

3. Operational Efficiency
It determines how effectively an individual is utilizing the organizational resources. If operational efficiency is lacking, it will lead to weak growth and low profit. The sub-elements of operational efficiency are:
Account receivable turnover: It determines the effective management of credit spread to customers. High credit numbers portray effective management of credit, while low numbers are a sign of the need for improvement in credit collection.

Inventory turnover: It determines the effective management of inventory. A high number is good, whereas a lower number depicts overproduction or selling mismanagement for the present sales level.
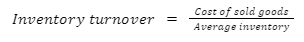
4. Capital Efficiency and Solvency
Investors and lenders mainly use it for the company’s revenue generation. Its sub-elements are:
Return on Equity: Determines the return generated by investors from your business.

Debt on Equity: Determines how much leverage you put into operating the business.

5. Liquidity
Determines the availability of enough funds or other assets to fulfill cash expenses such as bills and debts.
Current ratio: Evaluates the desired amount to be paid from cash available. If the ratio is below 1, it indicates inadequate liquidity and requires more cash to pay debts. If the ratio is above two, it is beneficial.

Interest covered: Calculation to pay off interest from available cash

Importance of Financial Analytics in Modern Business
Here are the importance of financial analytics in the rise of modern businesses.
- Aids organizations to discover the associated risks and correct the same
- Modifies and extends business processes to make them run smoothly
- Helps analyze if the organization’s investments are in the right direction
- Leverage big data and helps in building strategies to resolve problems and support business decisions
- Assess the level of profitability of the product in different aspects, including sales, customers, and future market
- Enables continuous visibility into operational and financial performance to prevent costly turnovers and losses in the future
- Helps analyze historical data and detect data gaps to correct the quality of data management and improve the overall performance of the business
- Allows identifying trends or patterns of business and work accordingly for efficient marketing
- Enables real-time adjustments to inject new flexibility into budget and forecasting
- Reduces fraud and removes manual, repetitive tasks, and increases efficiency
Types of Financial Analytics
The different types of financial analytics are as follows:
- Horizontal Analysis: It aids in calculating financial statements of the line of products with the base year. Here, you can compare the provided period’s figure with another period.
- Vertical Analysis: This method evaluates line items on balance sheets or income statements by representing each item as a percentage.
- Trend Analysis: This involves finding patterns of multiple periods and plotting those assessed patterns in graphical form to make an informed decision.
- Solvency Analysis: Long-term analysis involves a quick review of a company’s solvency to check if the company can pay obligations and long-term liabilities completely.
- Profitability Analysis: The analysis aids in understanding the methods of revenue generation by the company.
- Liquidity Analysis: This helps in verifying if suitable liquidity is maintained throughout the given time where liabilities are meeting without any error.
- Variance Analysis: Business works on budgets and estimations after transaction completion. The variation between the budget and the actual cost is important to analyze. It helps prevent gaps in the process and make decisions not to repeat it.
- Scenario & Sensitivity Analysis: Several alterations occur in business relying on economic conditions, such as banking rates and tax structures. Thus, the treasury department conducts the analysis to assess each factor influencing the company’s financials.
- Valuation Analysis: The analysis aids in deriving a fair valuation of the organization or company and can be performed by tools like SOTP valuation and the dividend discount model.
- FP&A Analysis: Financial Planning and Analysis departments are prudent in every organization that checks data points of internal organization. They generate a Management Information System (MIS) to report to top management so they can take preventive measures to stay clear of major complications.
Top Financial Analytics Tools and Technologies
Financial analysis tools and software speed up the report generation and showcase the data in graphical form to enhance readability and ease of interpretation in comparison to tables in spreadsheets. Here are some of the top-notch financial analysis software:
IBM Cognos Finance
The financial tool delivers outstanding data analysis potentials for sales, workspace management systems, and supply chain procurement. The software supports closing, reporting, and consolidating processes with cloud-based solutions’ affordability and agility.
SAS Business Analytics
The software presents an integrated environment for simulation, text mining, data mining, predictive modeling, and descriptive modeling. Predictive modeling predicts future results, whereas descriptive determines historical events and relationships due to which they are generated.
NetSuite
The cloud-based Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software provides financial dashboards, analytic functions, and reporting that permits real-time monitoring of personal key performance indicators. It also aids in raising efficiency and productivity by connecting, automating, and easing operating and accounting processes.
Tableau
The tool holds importance in financial analytics as it generates an interactive dashboard for decision-making. The data can be quickly visualized, analyzed, and shared effortlessly. This data visualization tool helps in analysis by finding trends and patterns that provide valuable insights to make informed decisions.
Oracle Financial Analytics
The software is a suite of applications that offer multiple ways to connect, prepare, and observe data and covers risk, performance, compliances, financial crimes, customer insights, and regulatory reporting functions. The software permits insights into the general ledger and offers visibility into performance with respect to the budget.
How Do You Apply Financial Analytics?
Financial analytics is applicable to both individuals and organizations. It serves both parties through either of the three methods, depending on the requirement:
Sell Enhancement: Financial service agents and others use financial analytics to sell bond and stock investments. They also make predictions of the timings to sell, purchase, or hold the stocks.
Purchase Optimization: Insurance companies, private equity firms, or other related organizations generating investment strategies use financial analytics to make accurate and efficient investments. The purchase leads to maximum profitability and returns.
Investment: The mergers and acquisitions utilize financial analytics to make decisions based on economic conditions and evaluate the decision's potential success.
Key Challenges in Financial Analytics
The common challenges in financial analytics are:
- Inability to remain always updated with real-time information
- Inconsistent and unreliable financial processes can lead to inaccurate forecasting and budgeting
- Lack of effective business insights due to poor quality of data availability and data mismanagement
- Relying on web complex financial system that needs to be corrected otherwise may produce inaccurate results
- Keeping up with the updated regulatory compliances
- Continuous efforts for monitoring important data are required to avoid cyber threats and fraud
- Real-time analysis requires talent and technology. There is a shortage of both. The available technologies are quite expensive.
- Global economic uncertainty affects financial sectors. Applying accurate predictive models is crucial for setting up long-term financial goals.
Future of Financial Analytics
In the growing world of business, there is a demand for financial analytics to eliminate the gaps in data and improve the efficiency of business to make it run smoothly and gain more profitability. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics, there is an expected 9% increase in career growth in financial analytics, with an estimated 32,000 new job opportunities every year in the current decade. Moreover, presently, financial analytics holds an average salary of $91,580 per annum and has a wide scope of increment in the future based on higher demands. Financial analytics development is due to continuous growth in the global market, economic landscape alterations, and technological and innovation updates.
Enroll in the Professional Certificate Program in Business Analytics to learn over a dozen of data analytics tools and skills, and gain access to masterclasses by IBM experts, exclusive hackathons, and Ask Me Anything sessions.
Conclusion
Financial analytics plays a crucial role in business development. With the increase in the business market, updated trends, and technologies, there is an increase in the complexity of data, risk of potential fraud, data mismanagement, financial risks, and others. Handling these for visualization analysis and prediction strategy is possible only by financial analytics professionals. A career in financial analytics brings a bright future ahead.
Enroll in Simplilearn’s Professional Certificate Program In Business Analytics & Generative AI in collaboration with IBM. Master the skills and ride the wave of automation and transformation!
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is financial analytics a good career?
Yes. With a growing business, there is a demand to handle, manage, and analyze data requiring financial analytics, making it one of the top coveted career paths in the financial services industries.
2. What is the primary goal of financial analytics?
Financial analytics focuses on shaping business strategies via reliable, realistic, and actionable insights instead of intuition. Additionally, it removes data mismanagement and financial risk to make the business run efficiently.
3. What distinguishes financial analytics tools from traditional financial analysis tools?
Traditional financial analysis tools are more focused on simple analysis, often done through mathematics and statistics. Their emphasis is only on finances, and common examples are spreadsheets and financial ratios. Financial analytics include both finance-based analysis and business-driven growth. They comprise advanced tools and offer predictive analytics. The common examples are Tableau and SAP.
4. Do financial analysts use Python?
Yes. Financial analytics uses the computer language Python in quantitative finance to analyze big datasets of large financial data to simplify the visualization process.
5. Can financial analytics predict financial crises?
Yes. Financial analytics predicts financial crises based on historical datasets of location and business.
6. What abilities are required to succeed in financial analytics?
The abilities needed to succeed in financial analytics are critical thinking, problem-solving skills, accounting skills, knowledge of tools and technologies, understanding trends and patterns in business, a strong command of programming languages, and presentation skills.
7. What impact has AI had on financial analytics?
Artificial intelligence (AI) enhances the quality of financial statements, data, and financial risk management, which further aids by predicting market sentiments, identifying the latest market trends and patterns, making the right investment decisions, risk analysis, anti-money laundering (AML), security, and regulatory compliance.
