What is metadata management?
Before shedding light on metadata management, it is crucial to understand what metadata is. Metadata refers to the information about your data. This data includes elements representing its context, content, and characteristics. It helps you discover, access, use, store, and retrieve your data, having a wide spread of variations.
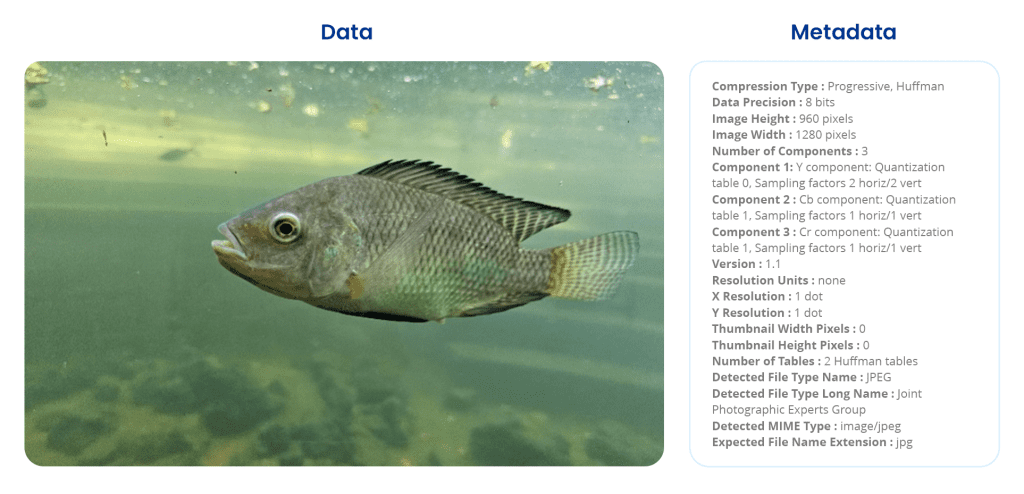
Metadata of an image. Image by Astera.
Let’s look at some of the metadata types below:
- Operational metadata: details how and when data occurs and transforms. This metadata type helps to manage, monitor, and optimize system architecture performance. Examples include time stamps, execution logs, data lineage, and dependency mapping.
- Legal metadata: involves the legal aspects of data use. This variation aims to protect data creators and regulate how one uses data. Examples include copyrights, licensing, and usage rights.
- Descriptive metadata: describes content (what, when, where, and who). It helps to identify, discover, find, and use data resources. Examples include title, author, keywords, and summary.
- Technical metadata: includes technical details of the data file. This metadata variation ensures proper data interpretation by software programs. Examples include file size, format (pdf, jpeg), encoding (UTF-8), and compression type.
- Process metadata: tracks data handling steps. It ensures data quality and reproducibility by documenting how the data was derived and transformed, including its origin. Examples include actions (such as data cleaning steps), tools used, tests performed, and lineage (data source).
- Preservation metadata: preserves data for long-term access, ensuring it remains usable over time by providing information for future care. Examples include backup location, migration history (format changes), and digital signatures.
-
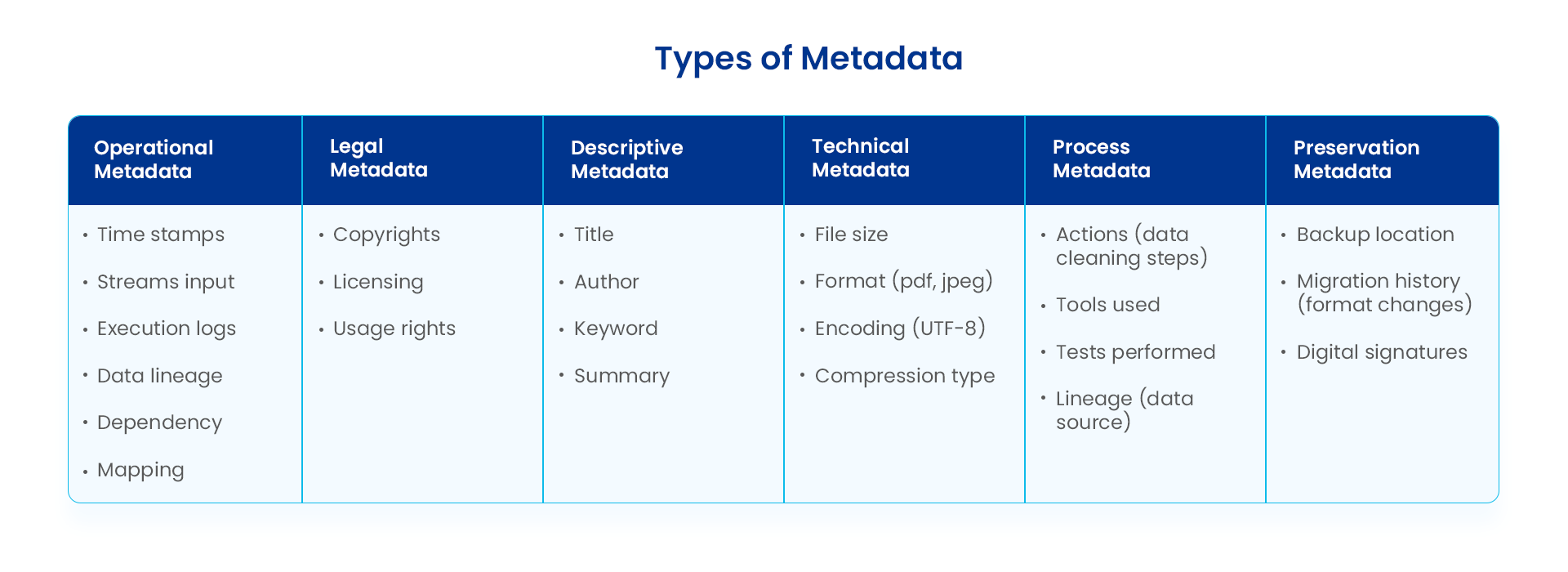
Types of metadata. Image by Astera.
To help you simplify your journey to metadata management, we will delve into the notion, explaining its significance, various types, how to structure it for optimal results, the value you will gain, what tools are involved, and how you can choose a fitting one, along with best practices ensuring value maximization. Let’s start with the basics.
Metadata management is the “practice” of managing data about data.
Metadata management helps create a common language for your data. In other words, it standardizes your data by collecting, organizing, and maintaining it using a set of activities, policies, and technologies. As a result, your data becomes quick to discover, easier to understand, and more accessible by humans and machines.
Let’s take an example of a library catalog. A library wouldn’t just store books on random shelves; it would categorize them, label them, and have entries in a catalog system. Metadata management does the same thing for your data. It makes finding, interpreting, and using the metadata easier, helping you find what you need and ensuring it is error-free.
As a result, everyone working with the core of data, including tech experts, salespersons, managers, and search engines, can better maximize its benefits, driving informed decisions.
Example of metadata management
Imagine a vast library of movies and shows on streaming platforms like Netflix or Prime Video as your data collection. It contains an extensive variety of content. This content is your data. However, finding that perfect movie becomes daunting without a proper cataloging system.
This situation is where metadata management simplifies things. Each piece of content includes details such as title, genre, synopsis, actors, language, release date, and more—known as metadata. It functions like a detailed catalog entry, offering a quick guide for viewers to skim through the content and find what they like.
As stated above, streaming services leverage metadata management to effectively categorize content (metadata) by multiple variables. Metadata enables them to deliver personalized recommendations, custom playlists, and dynamic grouping of content—all driven by metadata analytics. Subsequently, this strategy personalizes the streaming experience to match users’ preferences, making it easier for them to explore new favorites and revisit cherished classics.
Master data management vs. Metadata management
Before proceeding, it’s essential to clarify that while both master data management (MDM) and metadata management are crucial components of data management and governance, they are two unique concepts and, therefore, not interchangeable.
Master data describes the core information necessary for the operations or transactions within a business. This data includes but is not limited to, the unique identifiers or attributes of business entities—for example, product IDs, customer names, and company branches. Master data management is a business function that aims to create a unified, accurate, and consistent view of this data. It involves collecting, cleaning, managing, sharing, and protecting this data to ensure everything runs smoothly.
Examples include information like file formats such as mp3 for audio files and pdf for documents, among others. Metadata management is the strategy that centers on organizing, managing, and governing metadata.
Why is metadata management important?
Data is only valuable if it is reliable. It isn’t easy to know whether it is accurate, up-to-date, or relevant without proper context. Metadata management is elemental in providing this context to data and is the cornerstone for effective data governance and intelligent data management, ensuring your data is reliable and authentic. Using precise policies and standards, this practice helps you manage data about your data (metadata) and monitors its quality and relevance, ensuring compliance with regulations.
Additionally, it uncovers insights that simplify data discovery, risks associated with it, its value, how to use it, and the relationship between data elements, enabling seamless data flow mapping. Moreover, when powered by AI and machine learning, metadata management solution terms as “active,”—meaning it attains potency to integrate with other applications, including data analytics programs and simultaneously gets enhanced by utilizing human knowledge, ultimately generating new and accurate insights.
Interrelation between metadata and other applications. Image by Astera.
Here are some of the questions different personas or teams within the same organization may ask themselves (thanks to metadata management) and assess their performance while ensuring a single source of truth for everyone:
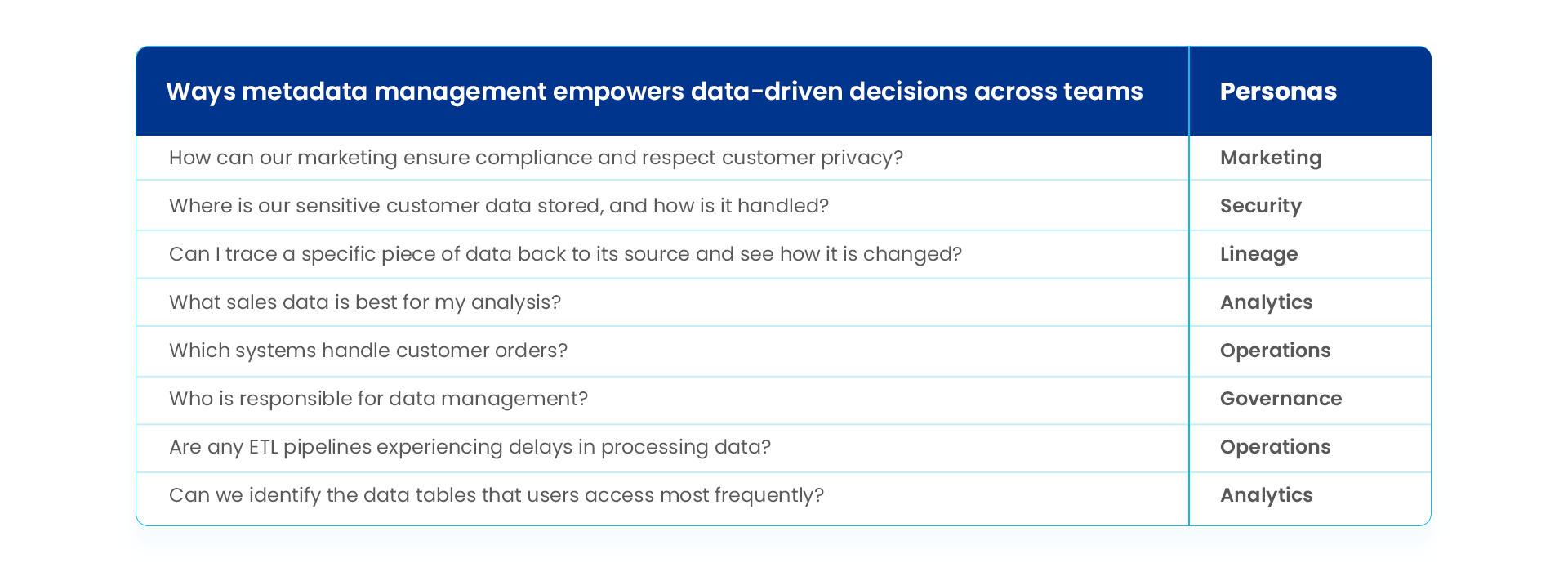
Ways metadata management empowers data-driven decisions across teams. Image by Astera.
These value additions are only the tip of the iceberg. With over 5.44 billion global internet users as of April 2024, the amount of data created, stored, copied, and consumed is expected to explode to 181 zettabytes by 2025. That said, aptly managing the metadata of such breadth is more crucial than ever.
Benefits of metadata management
Having received various names, from “the business glossary for data” and “data cataloging” to being known as “a single source of truth,” metadata management plays a pivotal role comparable to that of the Rosetta Stone in the realm of data.
It deciphers the meaning and context of data for everyone, just as the Rosetta Stone unlocked ancient Egypt’s history and culture, making it understandable. For a better understanding, let’s take a look at some of its benefits, making it indispensable for data-driven businesses:
- Data discoverability and usability
- Data consistency and unification
- End-to-end data lineage and governance
- Time and cost savings
- Data integration and collaboration
- Data discoverability and usability:
Metadata management is a comprehensive data catalog that allows you to discover relevant datasets. This discoverability increases accessibility, enabling better data utilization and informed decision-making.
- Data consistency and unification:
It establishes a standardized approach to defining data within an organization. Thus, each department has access to the metadata it needs to understand and manage its systems, data, and operations effectively. This practice fosters consistency, streamlines data governance, unifies the company’s approach to data, and leads to fewer data retrieval issues.
- End-to-end data lineage and governance:
Metadata management records a dataset from its origin to each transformation it undergoes. These detailed logs help track data for regulations and perform data quality assessments and root cause analysis, ensuring data quality and risk mitigation.
- Time and cost savings:
Automating and standardizing metadata management allows companies to reallocate their resources to high-priority tasks. This practice saves the resource time previously spent on manual tasks. Additionally, it leads to savings in areas like data design, conversion, and mapping.
- Data integration and collaboration:
Metadata management allows seamless integration into various sources, systems, and applications by documenting data structures, formats, content, and relationships. Additionally, it helps grasp the connections and dependencies between different data assets, ensuring integration and collaboration across departments.
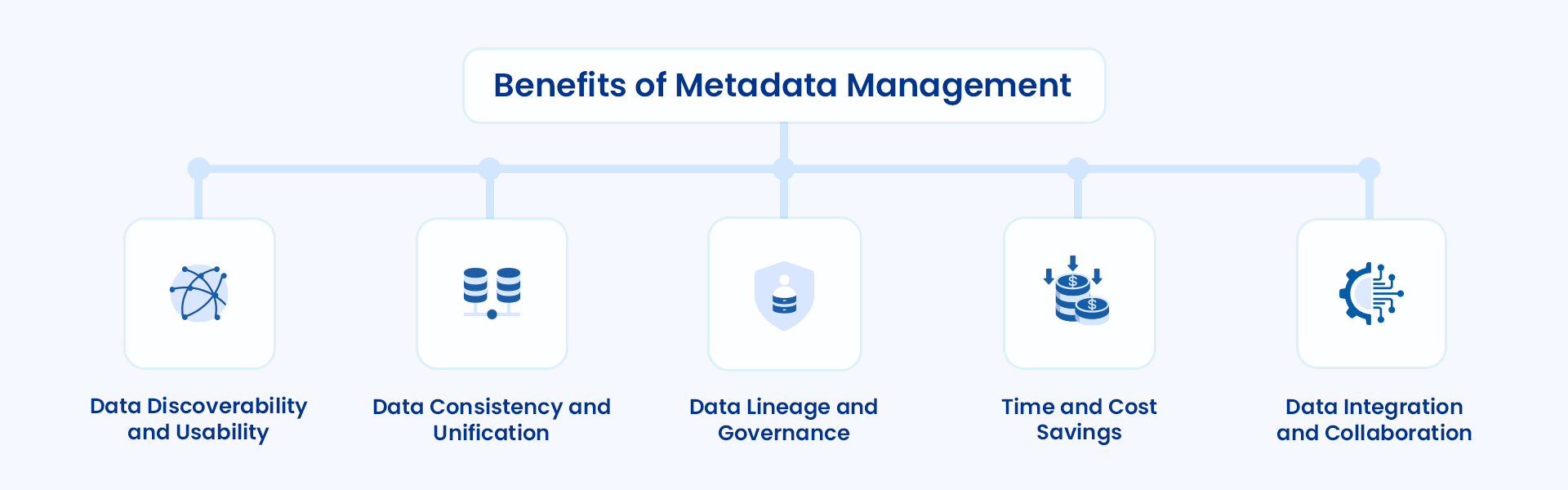
Benefits of metadata management. Image by Astera.
Due to such meaningful contributions, the metadata management market growth is surging globally, showing an impressive compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.18% from 2023 to 2028.
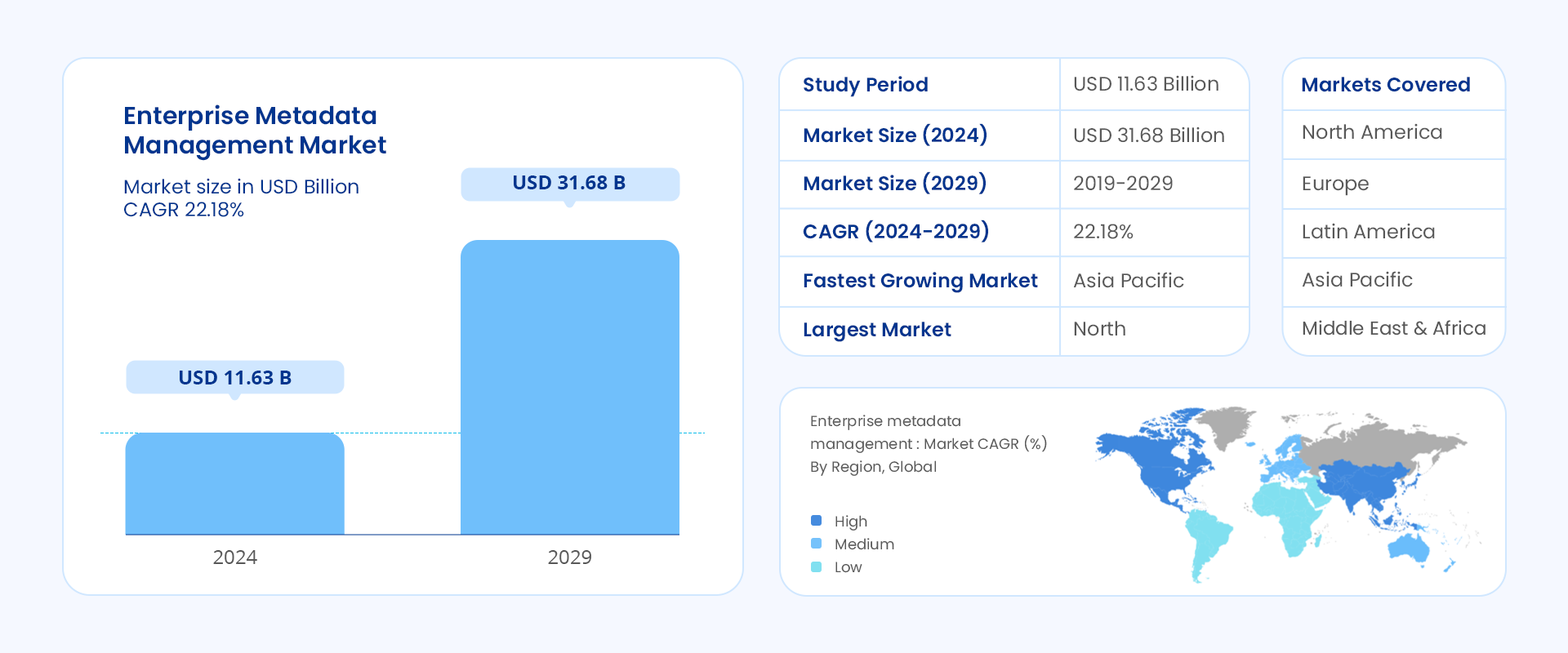
Enterprise metadata management market – Growth rate by region. Source: Mordor Intelligence.
How does metadata management work?
Effective data utilization hinges on a solid data foundation. Metadata management provides this concrete shared foundation by organizing and comprehending data metadata. Here’s a breakdown of how it works:
Step 1: Metadata collection
It begins by collecting metadata from various data sources, including on-premises and cloud systems. These data sources include data lakes, warehouses, databases, file systems, applications, and data integration tools. This process aims to accurately understand the data’s structure, format, and content, ensuring its reliability and suitability for analytics and data science initiatives.
Step 2: Metadata curation
After collection, the raw metadata is curated with relevant business context for shared understanding. It is categorized and organized by purpose and usage, enriched with attributes and relationships. This data is then cataloged in a central repository, ensuring it is searchable and accessible. Furthermore, user feedback, including ratings, reviews, and certifications, further enhances its value by providing insights into its usefulness to others.
Step 3: Intelligent metadata management
The final step, intelligent metadata management, uses AI and machine learning to analyze these datasets deeply. These technologies examine metadata to discover data lineage, reveal hidden connections, and identify similar datasets, ranking them as per user needs. This process facilitates users with the discovery of the most relevant information for any given task. Ultimately, this approach transforms raw data into a strategic asset, empowering confident, data-driven decisions.
What is a metadata management framework (MMF)?
Metadata management framework refers to an organization’s approach to creating, processing, governing, and utilizing its metadata. This framework encompasses the following components:
- Goal and objective: Identifying a focused area you’re trying to solve or improve.
- Stakeholders: Engaging relevant data owners from the beginning ensures the framework is shaped correctly from the start.
- Strategy: Defining the types of metadata that you will work on and setting priority goals and objectives for metadata management.
- Architecture: Outlining standards, models, and guidelines to ensure a unified approach across the organization.
- Processes: Creating processes and workflows for collecting, documenting, and maintaining metadata with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Tools and Technologies: Selecting and implementing tools and technologies that are easy to use, allow dataset standardization, and align with your organization’s requirements and goals for data cataloging, modeling, repositories, profiling, and lineage.
- Integration: Ensuring your metadata integrates with the existing tech stack.
- Governance: Establishing metadata governance processes to ensure metadata integrity, security, and compliance. Additionally, setting up a data governance body to oversee your metadata management framework and resolve conflicts.
- Training and education: Offering training and education to enhance awareness and competencies in metadata management. This practice includes a comprehensive program that informs stakeholders about metadata management’s importance, their roles, and the use of established tools and processes.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly assessing and enhancing the framework based on user feedback and observed usage trends.
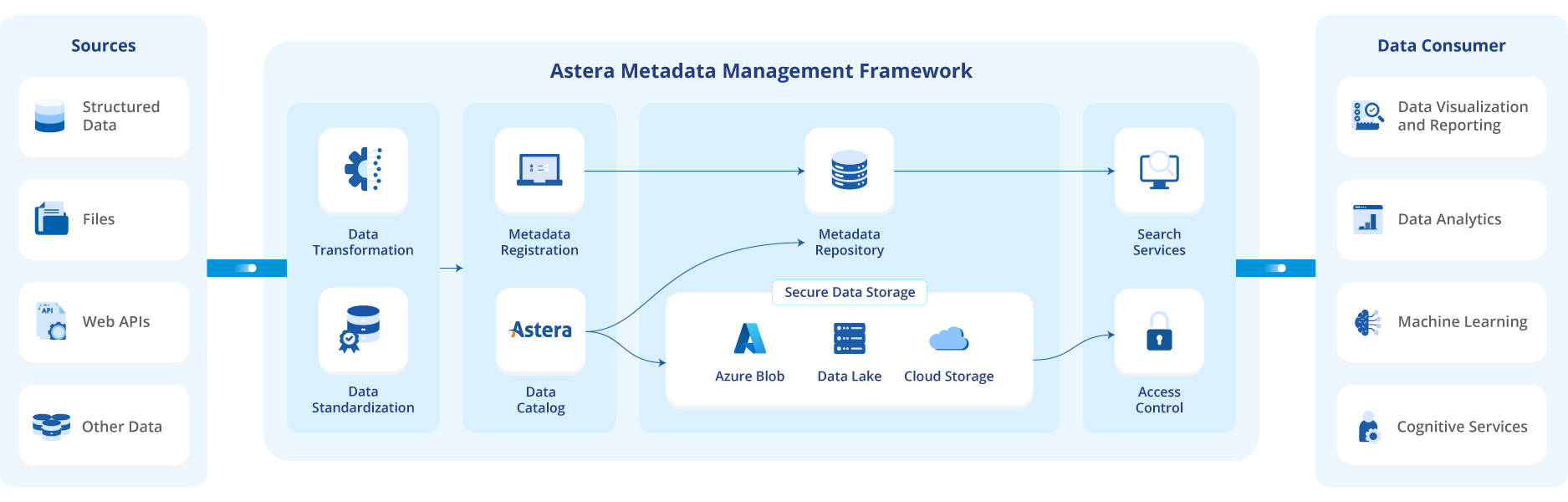
Astera Metadata Management Framework
Metadata management use cases
Effective metadata management unlocks a wide range of functionalities for organizations. Let’s explore some of these applications:
- Improved efficiency and troubleshooting
- Enhanced data analytics
- Data utilization and cost-optimization
- Automated data security and compliance
- Effective data governance
- Streamlined onboarding and integration
- Improved efficiency and troubleshooting:
Automated lineage tracking, a vital metadata management component, visualizes data flow from its origin to any transformations it undergoes. This approach empowers data teams to analyze root cause with lightning speed by pinpointing the exact source of problems within queries or reports. As a result, it saves a significant chunk of time for data professionals, improving problem-solving capabilities across the team.
- Enhanced data analytics:
Well-managed metadata is fundamental to delivering quality and consistency – the prerequisites of effective data analytics. It facilitates self-service analytics and business intelligence initiatives by making data assets more readily discoverable and accessible to business users, fostering a data-driven culture.
- Data utilization and cost-optimization:
By analyzing usage patterns, such as identifying frequently or infrequently accessed tables or inefficient queries, metadata management enables organizations to make informed decisions on optimizing their data storage and processing resources. These insights allow cost-saving costs and enhanced data warehouse efficiency.
- Automated data security and compliance:
Metadata management is critical in automating data classification in line with regulatory requirements (e.g., PII under EU GDPR or internal team data). This mechanism enforces security protocols, helping organizations maintain compliance and data security while reducing risks associated with data breaches.
- Effective data governance:
Data governance requires a comprehensive view of data to realize its potential fully. Metadata management enables this, managing the entire data lifecycle while ensuring its quality, accessibility, availability, and security.
- Streamlined onboarding and integration:
An enterprise metadata management software provides end users direct access to relevant metadata within their tools, simplifying onboarding processes and organizational integration for new employees.
Metadata management tools
A metadata management tool is software designed to help organizations collect, organize, store, and manage metadata efficiently. These tools enable organizations to fully understand and leverage their data, providing a centralized system for cataloging, monitoring, and analyzing data lineage, relationships, and usage patterns.
Capabilities of a metadata management solution
Metadata management tools encompass many features like data catalog, business glossary, data lineage, data profiling, interoperability, and impact analysis. Their market is expected to go through a compound annual growth rate of 18.4% by 2029.
Although these tools offer numerous benefits, it is essential to carefully assess the program before adopting one. Here are some of the capabilities to look for in a metadata management solution:
- Data inventory:
What data do you have, and where is it stored?
Data inventory, also known as data mapping, acts like a directory, listing all your organization’s data assets and where they’re stored. This granular view facilitates data governance by ensuring response data usage.
For instance, you can track how the data you retrieved (i.e., response data) from the metadata research (e.g., customer names) is used later. This capability lets you see who is accessing the data, how the respective person uses it, and its impact on the data (data lineage).
- Data catalog:
Where is our data, and how can we access it?
Unlike data inventories, data catalogs are like advanced search engines for your data. These automated tools actively scan and catalog data across various storage locations – databases, data lakes, and data warehouses – making it much easier for business users to discover the specific datasets they need.
- Data lineage:
Where has our data been, and what changes did it go through?
Data lineage acts like a behind-the-scenes map for your data. It tracks the journey of your data from its origin (i.e., source) through any transformation it undergoes to where it is ultimately used (i.e., destination). This information is beneficial for impact analysis, where you must predict the consequences of changes to data sources or processing methods.
- Tagging
How can we enrich and adapt our data for future needs?
Tagging involves assigning relevant labels, called metadata tags, to data inventory to categorize and describe them with keywords, making them highly searchable and adaptable to changing business needs. Some tools can even automate tagging based on patterns, saving time and reducing errors.
- Data matching
How can we ensure our metadata accurately reflects data asset relationships?
Data matching helps identify connections between different pieces of metadata. Take an example of two datasets that might have similar information but slightly differ in names or formats. Metadata management tools with built-in data matching capability automatically compare these datasets and identify potential matches, making your data searches more accurate.
- Collaboration
What does our data mean (offer context) to our teams?
Effective metadata management requires clear communication between teams about data definitions and usage. So, collaboration features like commenting, annotations, and version control create a central platform for dialogue on these aspects. For which documenting every interaction among teams is vital and must be offered by the metadata management solution. This transparency fosters knowledge sharing, helps address inconsistencies in data understanding, and ultimately leads to better, data-driven decisions.

Six questions to ask when choosing a metadata management tool. Image by Astera.
Metadata management best practices
Here are some of the ways you can utilize to maximize your metadata management value and its sustainability:
- Establish a unified metadata foundation: Create a central repository for metadata to provide insights across all data management practices.
- Harness the power of all six metadata categories: Drive metadata-driven intelligence by capturing the six metadata categories – operational, legal, descriptive, technical, process, and preservation – to maximize the value of your data.
- Integrate AI/ML to augment your metadata management: Leverage AI/ML on top of your unified metadata foundation to make cloud data processes intelligent and adaptable.
- Empower users with an AI-powered data catalog: Capture and enrich enterprise metadata with business context using an AI-powered data catalog, making relevant data discoverable, accessible, understandable, and trustworthy.
- Ensure scalable and comprehensive metadata management: Achieve unparalleled management of metadata, offering extensive connectivity across multi-cloud, on-premises environments, applications, and ETL/BI tools; deep metadata extraction and data lineage comprehension capabilities (e.g., through database code parsing) and scalability to support millions of metadata assets, fulfilling the demands of the modern data landscape.
- Govern AI/ML models effectively: Establish governance for AI/ML models by managing their metadata, enabling performance measurement against business objectives, and mitigating algorithmic biases.
- Establish a metadata leadership program: Ensure metadata leaders are part of the governance team to operationalize metadata management policies, fostering success through leading by example.
- Invest in an appropriate metadata management tool: Once you have finalized your metadata strategy, scope, roles, and standards, you’ll be equipped to identify the essential features your business requires in a metadata management system. This analysis may lead you to acquire a new, dedicated tool or leverage existing metadata repositories within your current data management or business intelligence tools.
- Maintain consistency across the organization: Once initiated, consistently create metadata following policies and standards and communicate its significance to all data users and stakeholders, ensuring their commitment and engagement.
Final Words
Like a map empowers exploration, well-managed metadata helps maximize your data value. Metadata management establishes a standardized approach for describing and organizing your data assets. It enhances data discoverability and understanding, enhancing informed decision-making at all levels.
Astera’s metadata-driven data warehousing tool helps you prioritize metadata management by automating your metadata’s discovery, categorization, and management. It provides enterprise-wide shared data understanding, making your metadata easily searchable and readily interpretable.
At Astera, we help organizations unlock the true potential of their data and establish data-driven success. Request a live product demonstration to see it in action, or get in touch with our experts to explore how Astera DW Builder can easily enrich your metadata infrastructure!
Automate Metadata Management with Astera Unified Metadata-Driven Solution
By automating metadata discovery, categorization, and management, Astera creates a standardized approach that improves data discoverability and understanding — fostering informed decision-making across all organizational levels.
Explore how our metadata-driven tool works.
Download Free 14-Day Trial











